Page 46 - Low Carbon Development in China and India
P. 46
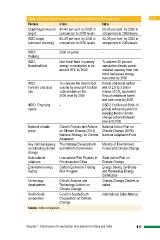
Table 1.2 Policy Objectives and Low Carbon Development in China and India 1.0
Themes China India
Copenhagen Accord 40–45 per cent by 2020 in 20–25 per cent by 2020 in
target comparison to 2005 levels comparison to 2005 levels
INDC target 60–65 per cent by 2030 in 33–35 per cent by 2030 in
(emission intensity) comparison to 2005 levels comparison to 2005 levels
INDC: 2030 or earlier -
Peaking
Non-fossil fuels in primary To achieve 40 percent
INDC: energy consumption to be cumulative electric power
Non-fossil fuel around 20% by 2030 installed capacity from non-
fossil fuel based energy
INDC: To increase the forest stock resources by 2030
Forestry and land volume by around 4.5 billion
use cubic meters on the Create additional carbon
2005 level by 2030 sink of 2.5 to 3 billion
INDC: Financing ttohnronuegshoafdCdOiti2oenqaul ifvoarelesntt
needs - and tree cover by 2030
National climate China’s Policies and Actions USD 2.5 trillion (at 2014-15
policy on Climate Change (2014) prices) will be required for
National Strategy for Climate meeting India’s climate
Key national agency Adaptation change actions between
coordinating climate now and 2030.
change The National Development
Sub-national and Reform Commission National Action Plan on
initiatives Climate Change (2008)
Emissions/ energy Low-carbon Pilot Projects in National Adaptation Fund
trading Provinces and Cities
Ministry of Environment,
Carbon Emissions Trading Forest and Climate Change
Pilot Program
State Action Plan on
Technology China’s Science and Climate Change
development Technology Actions on
Climate Change Energy Saving Certificate
and Renewable Energy
South-South Fund for South-South Certificates
cooperation Cooperation on Climate
Change Climate Change Centers in
states
International Solar Alliance
Source: Author compilation
Chapter 1 Dimensions of Low Carbon Development in China and India 11
Themes China India
Copenhagen Accord 40–45 per cent by 2020 in 20–25 per cent by 2020 in
target comparison to 2005 levels comparison to 2005 levels
INDC target 60–65 per cent by 2030 in 33–35 per cent by 2030 in
(emission intensity) comparison to 2005 levels comparison to 2005 levels
INDC: 2030 or earlier -
Peaking
Non-fossil fuels in primary To achieve 40 percent
INDC: energy consumption to be cumulative electric power
Non-fossil fuel around 20% by 2030 installed capacity from non-
fossil fuel based energy
INDC: To increase the forest stock resources by 2030
Forestry and land volume by around 4.5 billion
use cubic meters on the Create additional carbon
2005 level by 2030 sink of 2.5 to 3 billion
INDC: Financing ttohnronuegshoafdCdOiti2oenqaul ifvoarelesntt
needs - and tree cover by 2030
National climate China’s Policies and Actions USD 2.5 trillion (at 2014-15
policy on Climate Change (2014) prices) will be required for
National Strategy for Climate meeting India’s climate
Key national agency Adaptation change actions between
coordinating climate now and 2030.
change The National Development
Sub-national and Reform Commission National Action Plan on
initiatives Climate Change (2008)
Emissions/ energy Low-carbon Pilot Projects in National Adaptation Fund
trading Provinces and Cities
Ministry of Environment,
Carbon Emissions Trading Forest and Climate Change
Pilot Program
State Action Plan on
Technology China’s Science and Climate Change
development Technology Actions on
Climate Change Energy Saving Certificate
and Renewable Energy
South-South Fund for South-South Certificates
cooperation Cooperation on Climate
Change Climate Change Centers in
states
International Solar Alliance
Source: Author compilation
Chapter 1 Dimensions of Low Carbon Development in China and India 11