Page 267 - Low Carbon Development in China and India
P. 267
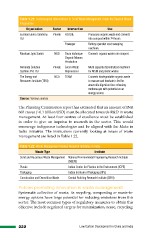
Table 1.21: Technological Interventions in Solid Waste Management Under the Swachh Bharat
Programme
Organization Sector Intervention Use
Ecoman Enviro Solutions Private FOODIE Processes organic waste and converts
Ltd into compost within 24 hours
Esweeper Battery operated road sweeping
machines
Muskaan Jyoti Samiti NGO Drum technique Converts organic waste into compost
Organic Manure
Production
NoKooda Solution Private Green Waste Multi capacity decentralized machines
Systems Pvt. Ltd Reprocessor for MSW and plastic wastes
The Energy and NGO TEAM Converts biodegradable organic waste
to manure and leachate is fed for
Resources Institute (TERI) anaerobic digestion thus releasing
methane gas with potential as an
energy source
Source: Various sources
The Planning Commission report has estimated that an amount of INR
600 crores (~0.1 billion USD) must be allocated towards R&D in waste
management. At least four centres of excellence must be established
in order to give an impetus to research in the sector. This would
encourage indigenous technologies and be aligned with the Make in
India initiative. The institutions currently looking at issues of waste
management are listed in Table 1.22.
Table 1.22: Waste Management Related Research Institutes in India
Waste Type Institute
Solid and Hazardous Waste Management National Environmental Engineering Research Institute
(NEERI)
Plastic Indian Center for Plastics in the Environment (ICPE)
Packaging Indian Institute of Packaging (IIPa)
Construction and Demolition Waste Central Building Research Institute (CBRI)
Policies promoting innovation in waste management
Systematic collection of waste, its recycling, composting or waste-to-
energy options have large potential for reducing emissions from this
sector. The most common types of regulatory measures to obtain this
objective include regulated targets for minimization, reuse, recycling;
232 Low Carbon Development in China and India
Programme
Organization Sector Intervention Use
Ecoman Enviro Solutions Private FOODIE Processes organic waste and converts
Ltd into compost within 24 hours
Esweeper Battery operated road sweeping
machines
Muskaan Jyoti Samiti NGO Drum technique Converts organic waste into compost
Organic Manure
Production
NoKooda Solution Private Green Waste Multi capacity decentralized machines
Systems Pvt. Ltd Reprocessor for MSW and plastic wastes
The Energy and NGO TEAM Converts biodegradable organic waste
to manure and leachate is fed for
Resources Institute (TERI) anaerobic digestion thus releasing
methane gas with potential as an
energy source
Source: Various sources
The Planning Commission report has estimated that an amount of INR
600 crores (~0.1 billion USD) must be allocated towards R&D in waste
management. At least four centres of excellence must be established
in order to give an impetus to research in the sector. This would
encourage indigenous technologies and be aligned with the Make in
India initiative. The institutions currently looking at issues of waste
management are listed in Table 1.22.
Table 1.22: Waste Management Related Research Institutes in India
Waste Type Institute
Solid and Hazardous Waste Management National Environmental Engineering Research Institute
(NEERI)
Plastic Indian Center for Plastics in the Environment (ICPE)
Packaging Indian Institute of Packaging (IIPa)
Construction and Demolition Waste Central Building Research Institute (CBRI)
Policies promoting innovation in waste management
Systematic collection of waste, its recycling, composting or waste-to-
energy options have large potential for reducing emissions from this
sector. The most common types of regulatory measures to obtain this
objective include regulated targets for minimization, reuse, recycling;
232 Low Carbon Development in China and India