Page 371 - Low Carbon Development in China and India
P. 371
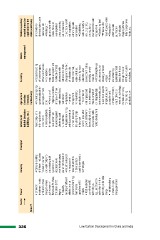
336 Sector Power Industry Transport Urban/rural Agriculture Forestry Waste Water resources/
habitat (includes (includes management coastal areas (as
buildings, etc.) livestock, • Capacity building applicable to the
horticulture) of forest managers, state conditions)
State officers and workers
• Vulnerability of rainwater for
Low Carbon Development in China and India • Enhanced • Capacity building made compulsory • Planning cropping mapping of the domestic water use in
investment in solar, of different industries to bring down the systems suitable for forest ecosystem and rural areas, etc.
wind and biomass focused on carbon consumption each agro-climatic livelihood of forest • Recharge of
energy to ensure and water footprints • Credit availability zone dependents with ground water with
achievement of and devising audit for rural infrastructure • Promotion of reference to climate special focus on
Renewable Purchase systems in all development and indigenous varieties change with the help over-exploited
Obligation (RPO) organizations to insurance against of crops which are of indicators like areas; promoting
targets monitor their usages climate induced water stress/flood/ forest cover map, soil conservation
• Capacity per unit of production vulnerabilities heat tolerant wasteland atlas, to avoid soil runoff,
building of different • Industries to pool • Regular monitoring • Agriculture vulnerability maps, soil degradation;
stakeholders on the resources in and documentation Information watershed atlas, enhancing water
generation, handling, research activities of urban landscape management: socioeconomic atlas, conservation
maintenance, to develop state- (including change For maximizing ethnicity, poverty • Establishing
operations of RE specific eco-friendly in land-use productivity even index etc. water authority to
projects technologies pattern), population in the context of • Promoting the use set up a pricing
• R&D to develop growth, settlements challenges posed of alternate source and regulatory
cost-effective RE (especially slums) to by climate change. of energy in forest mechanism for water
technologies, ensure sustainable Establishment of villages management
e.g., use of silicon habitat development an integrated data • Protecting • Developing ideal
rather than thin film centre whereby data and enhancing PPP models for
technologies for solar related to all aspects sustainable forest recycling waste water
energy of agriculture, such based livelihoods • Research on
• Institutionalizing as weather and through focus on effective water
biomass, biogas climate information, NTFP, eco-tourism, purification
energy generation crop biodiversity, silviculture, lac technologies,
research, technology, mapping of areas
markets, and policy likely to experience
for maximizing floods, etc.
productivity are
habitat (includes (includes management coastal areas (as
buildings, etc.) livestock, • Capacity building applicable to the
horticulture) of forest managers, state conditions)
State officers and workers
• Vulnerability of rainwater for
Low Carbon Development in China and India • Enhanced • Capacity building made compulsory • Planning cropping mapping of the domestic water use in
investment in solar, of different industries to bring down the systems suitable for forest ecosystem and rural areas, etc.
wind and biomass focused on carbon consumption each agro-climatic livelihood of forest • Recharge of
energy to ensure and water footprints • Credit availability zone dependents with ground water with
achievement of and devising audit for rural infrastructure • Promotion of reference to climate special focus on
Renewable Purchase systems in all development and indigenous varieties change with the help over-exploited
Obligation (RPO) organizations to insurance against of crops which are of indicators like areas; promoting
targets monitor their usages climate induced water stress/flood/ forest cover map, soil conservation
• Capacity per unit of production vulnerabilities heat tolerant wasteland atlas, to avoid soil runoff,
building of different • Industries to pool • Regular monitoring • Agriculture vulnerability maps, soil degradation;
stakeholders on the resources in and documentation Information watershed atlas, enhancing water
generation, handling, research activities of urban landscape management: socioeconomic atlas, conservation
maintenance, to develop state- (including change For maximizing ethnicity, poverty • Establishing
operations of RE specific eco-friendly in land-use productivity even index etc. water authority to
projects technologies pattern), population in the context of • Promoting the use set up a pricing
• R&D to develop growth, settlements challenges posed of alternate source and regulatory
cost-effective RE (especially slums) to by climate change. of energy in forest mechanism for water
technologies, ensure sustainable Establishment of villages management
e.g., use of silicon habitat development an integrated data • Protecting • Developing ideal
rather than thin film centre whereby data and enhancing PPP models for
technologies for solar related to all aspects sustainable forest recycling waste water
energy of agriculture, such based livelihoods • Research on
• Institutionalizing as weather and through focus on effective water
biomass, biogas climate information, NTFP, eco-tourism, purification
energy generation crop biodiversity, silviculture, lac technologies,
research, technology, mapping of areas
markets, and policy likely to experience
for maximizing floods, etc.
productivity are