Page 370 - Low Carbon Development in China and India
P. 370
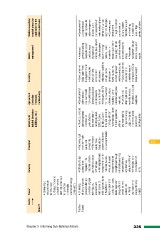
Chapter 3 Informing Sub-National Actions Sector Power Industry Transport Urban/rural Agriculture Forestry Waste Water resources/
habitat (includes (includes management coastal areas (as
• Climate change • Improving road buildings, etc.) livestock, applicable to the
aspects to be networks—both horticulture) state conditions)
State integrated in the quality and
• Earmarking a industrial policy to connectivity • Municipal demand • Development of • Development of • Awareness • Development of
Madhya marginal amount promote low carbon • Efficient and side management, watersheds and Sustainable Forest generation among a comprehensive
Pradesh from the cess/ technologies quality mass promotion of small catchments Management Plans people about best water data base for
surcharge of revenue • An integrated water transportation green, effective that would increase • Enhancing the practices, waste better management
collected from the management plan for systems with stress implementation of biomass production levels of forest segregation at of action plans,
electricity consumers industrial clusters on route optimization building by-laws, and increase the conservation/ sources, development and assessment of
for promotion • Industrial waste ECBC, National fertility of the soil afforestation/ of sites to explore water availability and
335 of renewable management to be Building Code of • Measures like SRI reforestation activities waste-to-energy demand by various
sources and energy strengthened through India and promotion for rice, raised bed through proper potential, more sectors in the future
conservation enhanced networking of energy-efficient cultivation, plastic demarcation of investment in • Command area
between different household appliances mulching, use of forest boundaries, research activities for development
• Enhancing organizations, • Strict regulations cultivars using lower connecting forest/ developing different through completion
efficiency in power using more efficient and their water, etc. wildlife corridors, etc. cost-effective models and renovation
generation through technologies, strict implementation to • Use of micro/ • Developing centres to convert waste to of canal systems,
promotion of green implementation of bring down energy drip irrigation to be of excellence‘ to energy field channels and
technologies, norms usage, energy audit extended to crops undertake research • Wastewater land levelling,
renovation and of commercial and like cotton, fruits, and on impacts of CC on management through rejuvenation of
maintenance of government vegetables forest ecosystem reduce, reuse, and lakes, village
existing power plants buildings to be recycle ponds, collection
• Reduction of
transmission and
distribution losses,
feeder separation,
energy-efficient
service delivery
systems, etc.
• Market
capitilazation for
energy efficiency
projects
3.3
habitat (includes (includes management coastal areas (as
• Climate change • Improving road buildings, etc.) livestock, applicable to the
aspects to be networks—both horticulture) state conditions)
State integrated in the quality and
• Earmarking a industrial policy to connectivity • Municipal demand • Development of • Development of • Awareness • Development of
Madhya marginal amount promote low carbon • Efficient and side management, watersheds and Sustainable Forest generation among a comprehensive
Pradesh from the cess/ technologies quality mass promotion of small catchments Management Plans people about best water data base for
surcharge of revenue • An integrated water transportation green, effective that would increase • Enhancing the practices, waste better management
collected from the management plan for systems with stress implementation of biomass production levels of forest segregation at of action plans,
electricity consumers industrial clusters on route optimization building by-laws, and increase the conservation/ sources, development and assessment of
for promotion • Industrial waste ECBC, National fertility of the soil afforestation/ of sites to explore water availability and
335 of renewable management to be Building Code of • Measures like SRI reforestation activities waste-to-energy demand by various
sources and energy strengthened through India and promotion for rice, raised bed through proper potential, more sectors in the future
conservation enhanced networking of energy-efficient cultivation, plastic demarcation of investment in • Command area
between different household appliances mulching, use of forest boundaries, research activities for development
• Enhancing organizations, • Strict regulations cultivars using lower connecting forest/ developing different through completion
efficiency in power using more efficient and their water, etc. wildlife corridors, etc. cost-effective models and renovation
generation through technologies, strict implementation to • Use of micro/ • Developing centres to convert waste to of canal systems,
promotion of green implementation of bring down energy drip irrigation to be of excellence‘ to energy field channels and
technologies, norms usage, energy audit extended to crops undertake research • Wastewater land levelling,
renovation and of commercial and like cotton, fruits, and on impacts of CC on management through rejuvenation of
maintenance of government vegetables forest ecosystem reduce, reuse, and lakes, village
existing power plants buildings to be recycle ponds, collection
• Reduction of
transmission and
distribution losses,
feeder separation,
energy-efficient
service delivery
systems, etc.
• Market
capitilazation for
energy efficiency
projects
3.3