Page 336 - Low Carbon Development in China and India
P. 336
major costs that are to be incurred to implement the activities stated in
the Green India Mission (GIM). The mission also aims at enhanced CO2
sequestration by 50–60 million tonnes in the year 2020.
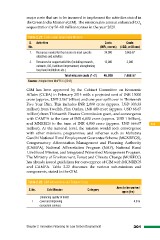
Table 2.21: Costs under Green India Mission Costs Costs
(INR, crores) (USD, millions)
S. Activities
No. 34,000 5,666.67
1. Resources needed for the mission to meet specific 12,000 2,000
objectives and activities
46,000 7,666.67
2. Resources for support activities (including research,
outreach, GIS, livelihood improvement, strengthening
local level institutions etc.)
Total mission costs (1+2)
Source: Adapted from MoEFCC (2013)
GIM has been approved by the Cabinet Committee on Economic 3.2
Affairs (CCEA) in February 2014 with a projected cost of INR 13000
crore (approx. USD 2.167 billion) and one year spill over in Thirteenth
Five Year Plan. This includes INR 2,000 crore (approx. USD 333.33
million) from Twelfth Plan Outlay, INR 400 crore (approx. USD 66.67
million) from Thirteenth Finance Commission grant, and convergence
with CAMPA to the tune of INR 6,000 crore (approx. USD 1 billion),
and MNREGS to the tune of INR 4,000 crore (approx. USD 666.67
million). At the national level, the mission would seek convergence
with other missions, programmes, and schemes such as Mahatma
Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS),
Compensatory Afforestation Management and Planning Authority
(CAMPA), National Afforestation Program (NAP), National Rural
Livelihood Mission, and Integrated Watershed Management Program.
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MOEFCC)
has already issued guidelines for convergence of GIM with MGNREGS
and CAMPA. Table 2.22 discusses the various sub-missions and
components, stated in the GIM.
Table 2.22: GIM Interventions and Tentative Costs
S.No. Sub Mission Category Area to be worked
upon (ha)
Enhancing quality of forest
4.9 m
1 cover and improving
ecosystem services
Chapter 2 Innovative Financing for Low Carbon Development 301
the Green India Mission (GIM). The mission also aims at enhanced CO2
sequestration by 50–60 million tonnes in the year 2020.
Table 2.21: Costs under Green India Mission Costs Costs
(INR, crores) (USD, millions)
S. Activities
No. 34,000 5,666.67
1. Resources needed for the mission to meet specific 12,000 2,000
objectives and activities
46,000 7,666.67
2. Resources for support activities (including research,
outreach, GIS, livelihood improvement, strengthening
local level institutions etc.)
Total mission costs (1+2)
Source: Adapted from MoEFCC (2013)
GIM has been approved by the Cabinet Committee on Economic 3.2
Affairs (CCEA) in February 2014 with a projected cost of INR 13000
crore (approx. USD 2.167 billion) and one year spill over in Thirteenth
Five Year Plan. This includes INR 2,000 crore (approx. USD 333.33
million) from Twelfth Plan Outlay, INR 400 crore (approx. USD 66.67
million) from Thirteenth Finance Commission grant, and convergence
with CAMPA to the tune of INR 6,000 crore (approx. USD 1 billion),
and MNREGS to the tune of INR 4,000 crore (approx. USD 666.67
million). At the national level, the mission would seek convergence
with other missions, programmes, and schemes such as Mahatma
Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS),
Compensatory Afforestation Management and Planning Authority
(CAMPA), National Afforestation Program (NAP), National Rural
Livelihood Mission, and Integrated Watershed Management Program.
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MOEFCC)
has already issued guidelines for convergence of GIM with MGNREGS
and CAMPA. Table 2.22 discusses the various sub-missions and
components, stated in the GIM.
Table 2.22: GIM Interventions and Tentative Costs
S.No. Sub Mission Category Area to be worked
upon (ha)
Enhancing quality of forest
4.9 m
1 cover and improving
ecosystem services
Chapter 2 Innovative Financing for Low Carbon Development 301