Page 260 - Low Carbon Development in China and India
P. 260
demonstration activities being undertaken by the Forest Research 3.1
Institute (FRI). In 2014, the Government has also initiated a national
Agroforestry Policy. It articulates the need for research on agroforestry
models suitable in the different climatic zones in the country.
Currently, over 30 Institutions under Indian Council for Agriculture
Research (ICAR) work on research on Agroforestry and they are co-
ordinated under Central Agroforestry Research Institute (CAFRI). Such
institutions must make the knowledge in the domain more robust and
should disseminate it through adequate extension services. Current
research includes agri-silviculture, silvipasture, silvi horticulture, social
sciences, watershed development, and human resource development
(CAFRI 2015). In addition, to promoting research in the forestry sector,
the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) to enable a decision
support system (DSS) has been initiated. Bhuvan, the geospatial portal
of the Indian Government enables sub-national governments to design
interventions and governance tools based on remote sensing. E-Green
Watch as an e-governance initiative has also enabled streamlining
and management of forestry works (SFR 2013). An Environmental
Information System (ENVIS) has also helped in creating the ecosystem
for policymakers, scientist and academicians to undertake research
which is multi-disciplinary and engages relevant stakeholders.
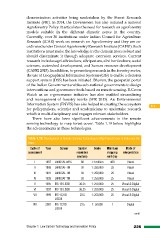
There have also been significant advancements in the remote
sensing technology to map forest cover. Table 1.19 below highlights
the advancements in these technologies.
Table 1.19: Development of Remote Sensing Technology to Map Forest Cover in India over the
Years
Cycle of Year Sensor Spatial Scale Minimum Mode of
assessment resolution mapping interpretation
(meters) unit (ha)
I 1987 LANDSAT-MSS 80 1:1 million 400 Visual
II 1989 LANDSAT-TM 30 1: 250,000 25 Visual
III 1991 LANDSAT-TM 30 1: 250,000 25 Visual
IV 1993 LANDSAT-TM 30 1: 250,000 25 Visual
V 1995 IRS-1B LISSII 36.25 1: 250,000 25 Visual & Digital
VI 1997 IRS-1B LISSII 36.25 1: 250,000 25 Visual & Digital
VII 1999 IRS-1C/1D 23.5 1: 250,000 25 Visual & Digital
LISSIII
VIII 2001 IRS-1C/1D 23.5 1: 50,000 1 Digital
LISSIII
contd...
Chapter 1 Low Carbon Technology and Innovation Policy 225
Institute (FRI). In 2014, the Government has also initiated a national
Agroforestry Policy. It articulates the need for research on agroforestry
models suitable in the different climatic zones in the country.
Currently, over 30 Institutions under Indian Council for Agriculture
Research (ICAR) work on research on Agroforestry and they are co-
ordinated under Central Agroforestry Research Institute (CAFRI). Such
institutions must make the knowledge in the domain more robust and
should disseminate it through adequate extension services. Current
research includes agri-silviculture, silvipasture, silvi horticulture, social
sciences, watershed development, and human resource development
(CAFRI 2015). In addition, to promoting research in the forestry sector,
the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) to enable a decision
support system (DSS) has been initiated. Bhuvan, the geospatial portal
of the Indian Government enables sub-national governments to design
interventions and governance tools based on remote sensing. E-Green
Watch as an e-governance initiative has also enabled streamlining
and management of forestry works (SFR 2013). An Environmental
Information System (ENVIS) has also helped in creating the ecosystem
for policymakers, scientist and academicians to undertake research
which is multi-disciplinary and engages relevant stakeholders.
There have also been significant advancements in the remote
sensing technology to map forest cover. Table 1.19 below highlights
the advancements in these technologies.
Table 1.19: Development of Remote Sensing Technology to Map Forest Cover in India over the
Years
Cycle of Year Sensor Spatial Scale Minimum Mode of
assessment resolution mapping interpretation
(meters) unit (ha)
I 1987 LANDSAT-MSS 80 1:1 million 400 Visual
II 1989 LANDSAT-TM 30 1: 250,000 25 Visual
III 1991 LANDSAT-TM 30 1: 250,000 25 Visual
IV 1993 LANDSAT-TM 30 1: 250,000 25 Visual
V 1995 IRS-1B LISSII 36.25 1: 250,000 25 Visual & Digital
VI 1997 IRS-1B LISSII 36.25 1: 250,000 25 Visual & Digital
VII 1999 IRS-1C/1D 23.5 1: 250,000 25 Visual & Digital
LISSIII
VIII 2001 IRS-1C/1D 23.5 1: 50,000 1 Digital
LISSIII
contd...
Chapter 1 Low Carbon Technology and Innovation Policy 225