Page 281 - Low Carbon Development in China and India
P. 281
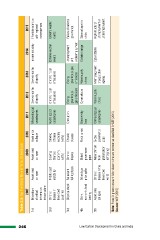
246 Table 2.2: Top Five Global Risks in Terms of Likelihoods
2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Meteorological Severe income Severe income Income disparity Interstate conflicts
1st Breakdown Asset price Asset price Asset price catastrophes disparity disparity with regional
Extreme weather consequences
of critical collapse collapse collapse Hydrological Chronic fiscal Chronic fiscal events
catastrophes imbalances imbalances Extreme weather
information Unemployment events
Corruption Rising Rising and
infrastructure greenhouse greenhouse gas underemployment Failure of national
gas emissions emissions Climate change governance
2nd Chronic Middle East Slowing Slowing Cyber attacks Water supply
disease in instability Chinese Chinese crises Cyber attacks State collapse or
developed economy economy Water supply crisis
countries (<6%) (<6%) crises Mismanagement
of population High structural
3rd Oil price shock Failed and Chronic Chronic ageing unemployment or
disease underemployment
failing states disease
Low Carbon Development in China and India 4th China Oil and gas Global Fiscal crises Biodiversity
economic hard price spike governance loss
landing gaps
5th Asset price Chronic Retrenchment Global Climatological
collapse disease in the from governance catastrophes
developed globalization gaps
world (emerging)
Note: Boxes in green represent risks related to the environment as classified in WEF (2015)
Source: WEF (2015)
2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Meteorological Severe income Severe income Income disparity Interstate conflicts
1st Breakdown Asset price Asset price Asset price catastrophes disparity disparity with regional
Extreme weather consequences
of critical collapse collapse collapse Hydrological Chronic fiscal Chronic fiscal events
catastrophes imbalances imbalances Extreme weather
information Unemployment events
Corruption Rising Rising and
infrastructure greenhouse greenhouse gas underemployment Failure of national
gas emissions emissions Climate change governance
2nd Chronic Middle East Slowing Slowing Cyber attacks Water supply
disease in instability Chinese Chinese crises Cyber attacks State collapse or
developed economy economy Water supply crisis
countries (<6%) (<6%) crises Mismanagement
of population High structural
3rd Oil price shock Failed and Chronic Chronic ageing unemployment or
disease underemployment
failing states disease
Low Carbon Development in China and India 4th China Oil and gas Global Fiscal crises Biodiversity
economic hard price spike governance loss
landing gaps
5th Asset price Chronic Retrenchment Global Climatological
collapse disease in the from governance catastrophes
developed globalization gaps
world (emerging)
Note: Boxes in green represent risks related to the environment as classified in WEF (2015)
Source: WEF (2015)