Page 248 - Low Carbon Development in China and India
P. 248
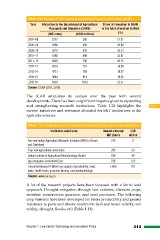
Table 1.11: Allocation to the Department of Agricultural Research and Education (DARE)
Year Allocation to the Department of Agricultural Share of allocation to DARE
Research and Education (DARE) in the total allocation to MoA
(INR crore) (USD million) (%)
2007–08 2337 390 21.21
2009–10 2960 493 20.69
2009–10 3210 535 20.24
2010–11 5386 898 22.61
2011–12 4929 788 20.76
2012-13 4510 752 18.59
2013-14 4731 789 18.57
2014-15 4884 814 18.35
2015-16 6320 1053 25.37
Source: CBGA (2011, 2015)
The ICAR articulates its success over the year with several 3.1
developments. There has been a significant impetus given to expanding
and strengthening research institutions. Table 1.12 highlights the
current initiatives and resources allocated for S&T institutions in the
agriculture sector.
Table 1.12: Current Initiatives on Expanding and Strengthening Agricultural Research Institutions
Institutions established Amount allocated USD
INR (crore) million
Two new Indian Agricultural Research Institutes (IARI) in Assam 100 17
and Jharkhand
Four new agricultural universities 200 33
Indian Institute of Agricultural Biotechnology, Ranchi 238 40
Agri education in the North East 738 123
Consortia Research Platform on aspects of productivity: Seed, 1,600 267
water, health foods, precision farming, and nanotechnology
Source: www.icar.org.in
A lot of the research projects have been focussed with a lab to land
approach. Drought mitigation through late varieties, alternate crops,
moisture conservation practices, and seed provision. The following
crop varieties have been developed for better productivity and greater
resistance to pests and abiotic constraints (soil and water salinity, soil
acidity, drought, floods, etc) (Table 1.13).
Chapter 1 Low Carbon Technology and Innovation Policy 213
Year Allocation to the Department of Agricultural Share of allocation to DARE
Research and Education (DARE) in the total allocation to MoA
(INR crore) (USD million) (%)
2007–08 2337 390 21.21
2009–10 2960 493 20.69
2009–10 3210 535 20.24
2010–11 5386 898 22.61
2011–12 4929 788 20.76
2012-13 4510 752 18.59
2013-14 4731 789 18.57
2014-15 4884 814 18.35
2015-16 6320 1053 25.37
Source: CBGA (2011, 2015)
The ICAR articulates its success over the year with several 3.1
developments. There has been a significant impetus given to expanding
and strengthening research institutions. Table 1.12 highlights the
current initiatives and resources allocated for S&T institutions in the
agriculture sector.
Table 1.12: Current Initiatives on Expanding and Strengthening Agricultural Research Institutions
Institutions established Amount allocated USD
INR (crore) million
Two new Indian Agricultural Research Institutes (IARI) in Assam 100 17
and Jharkhand
Four new agricultural universities 200 33
Indian Institute of Agricultural Biotechnology, Ranchi 238 40
Agri education in the North East 738 123
Consortia Research Platform on aspects of productivity: Seed, 1,600 267
water, health foods, precision farming, and nanotechnology
Source: www.icar.org.in
A lot of the research projects have been focussed with a lab to land
approach. Drought mitigation through late varieties, alternate crops,
moisture conservation practices, and seed provision. The following
crop varieties have been developed for better productivity and greater
resistance to pests and abiotic constraints (soil and water salinity, soil
acidity, drought, floods, etc) (Table 1.13).
Chapter 1 Low Carbon Technology and Innovation Policy 213